The lymphatic system collects extracellular fluid and returns it to the blood. Extracellular fluids that have entered the lymphatic system are called lymph.. The lymphatic system drains excess interstitial fluids, transports dietary lipids, and carries out immune responses. Lymphatic capillaries carry lymph through lymph nodes back to veinsIt is a low pressure system with one-way flow driven by skeletal and respiratory pumps. Valves within lymphatic vessels prevent back-flow, much as they do in the venous side of the circulation.
Pathogens are foreign materials that cause disease. They are removed by the immune system, which is anatomically part of the lymphatic system. Immune cells within the lymphatic system defend tissues from foreign substances. Organs of the lymphatic system are spleen, thymus, lymphatic vessels and nodes, and the tonsils. The major lymph nodes are located at the base of the neck (cervical), armpits (axillary), and groin (inguinal).
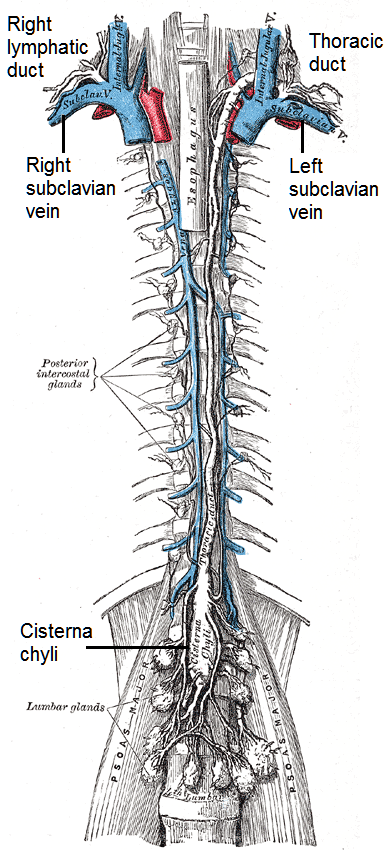
Lymph trunks are large lymphatic vessels. They collect lymph from lymphatic vessels in the lumbar and intestinal regions. The cisterna chyli collects lymph from the lower trunks and contains newly absorbed lipids. It forms the thoracic duct. Two lymph ducts collect fluids from lymphatic vessels and return it to the subclavian veins. The thoracic duct drains the lower body and the upper left side of the body. The right lymphatic duct drains the upper right side of the body.