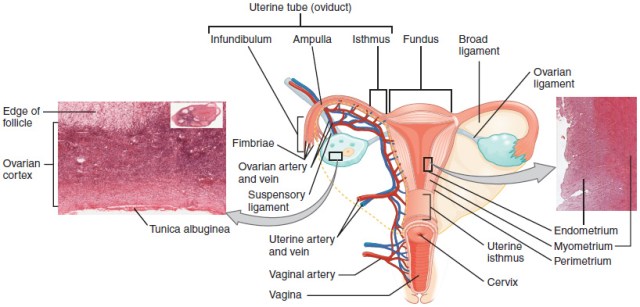
The external genital organs of the female are called the vulva. The mons pubis is fatty tissue covering the pubic symphysis. It is covered with hair, beginning at puberty. The labia majora are two large folds extending from the mons pubis to the perineum. The labia minora (inner labia) are smaller folds between medial to the labia majora that surround the vaginal opening. The clitoris is a button-like mass of erectile tissue superior to the urethral opening. The clitoral glans is its exposed tip.
The vestibule of the vagina surrounds the opening of the vagina and urethra. It lies between the labia minora. Within the vestibule is the hymen which partially covers the opening of the vagina. The vaginal orifice is the opening to the vagina. Between the clitoris and vagina is the external urethral orifice, the opening of the urethra. Near the urethral opening on the anterior wall of the vagina are the paraurethral glands (Skene’s glands). These may discharge water during sexual arousal. The vestibular glands (Bartholin’s glands) are near the vaginal orifice. They secrete a lubricating mucus.