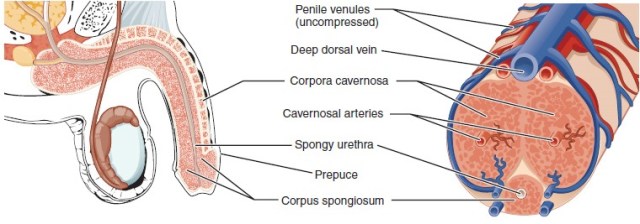
The penis is the external male intromittent organ, inserted to deliver sperm during copulation (sexual intercourse) to inseminate the female. The root of the penis is within the perineum (the region between the scrotum and the anus) and consists of a central bulb with lateral crura on each side. The body of the penis is external and ends in the glans penis, a sensitive, bulbous structure covered with foreskin (the prepuce) in uncircumcised males.
The body of the penis has two dorsal chambers (the corpora cavernosa), which fill with blood during an erection. A ventral corpus spongiosum surrounds the urethra and prevents it from closing during an erection.
Ejaculation has two phases. Sperm enter the vas deferens and pass into the urethra in anticipation of ejaculation (emission phase). Filling of the urethra with semen triggers contraction of skeletal muscles at the base of the penis. A sphincter at the base of the urinary bladder closes and semen is expelled from urethra (expulsion phase). The ejaculate has a volume of about 2.5 to 5 mL per, containing some 50-150 million sperm per mL. The rhythmic muscular contractions of ejaculation are associated with pleasure (orgasm).