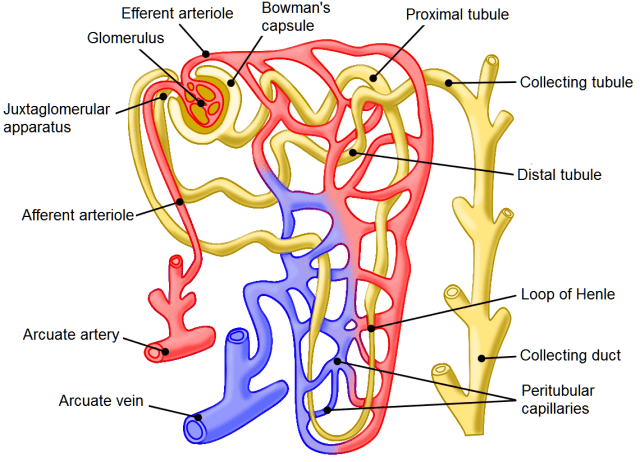
Nephrons are the functional units of the kidney. Arterial blood enters the nephron through the afferent arteriole. The afferent arteriole branches into a tuft of capillaries (glomerulus). Blood pressure forces fluids from the glomerular capillaries into Bowman’s capsule (glomerular filtration). From there, the urine passes through the proximal convoluted tubule, loop of Henle, and distal convoluted tubule to empty into the collecting duct. Within these tubes useful nutrients and water are reabsorbed and wastes either pass through or are secreted. This absorption and secretion also balances plasma electrolytes.
The cortical blood supply comes from the renal artery, which passes into the segmental, interlobar, arcuate, and cortical radiate (interlobular) arteries. The nephron blood supply begins with the afferent arteriole that enters Bowman’s capsule to form the glomerulus and leaves by the efferent arteriole which supplies the tubules with peritubular capillaries before returning to the venous system.