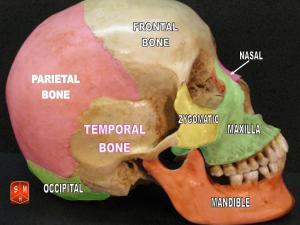
Anatomy (to cut up) studies biological structures and their relationships. It employs systematic observation, identification, and description. Typically, anatomy explores the structures of dead organisms (dissection). For example, anatomy gives names to the bones of the cranium: frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital.
Physiology (study of nature) concerns itself with the functions of the body. It explains how the anatomical parts work together to perform all the operations of the body. It is that part of the science of the body that carries out experimental investigations and provides theoretical explanations. Physiology typically studies living organisms (vivisection).
Anatomy (observation) and physiology (experiment) are complementary sciences: structures are adapted to specific functions. For example, cranial bones are thick and closely spaced. They are ideal for protecting the brain.
QBReview: Review this Lesson