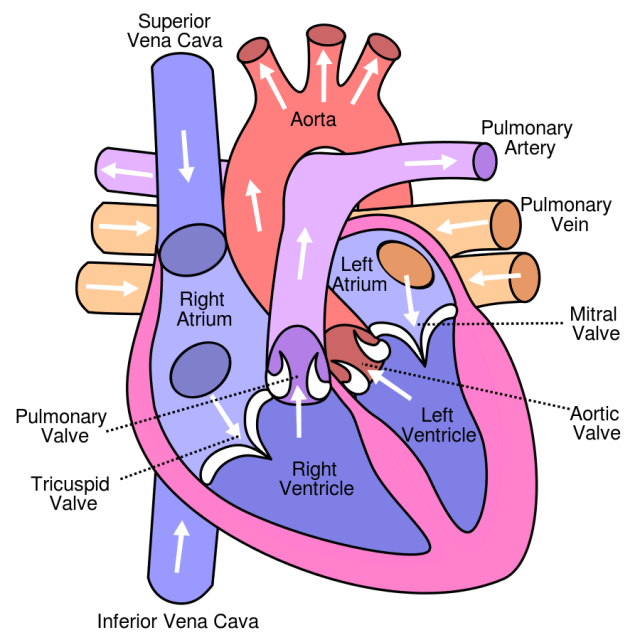
- Heart chambers are in pairs: left and right atria and ventricles (4 chambers in all).
- Atria receive blood from body and lungs and pump it into the ventricles.
- Auricles are small ear-shaped pouches that project from the upper portion of each atrium.
- Pectinate muscles are ridges of muscles in the atria that increase the strength of contraction with minimum muscle mass.
- The fossa ovalis is in the median wall of the right atrium; it is the remnant of the fetal formen ovale, a hole that allowed blood flow to bypassed the lungs in the fetus.
- Ventricles are the pumping chambers of the heart; they pump blood to the lungs and body.
- The left ventricle wall is thicker than that of the right ventricle because it pumps against higher pressure.
- The interventricular septum separates the right and left ventricles.
- Trabeculae carneae are ridges of muscle in the ventricles; their function is similar to that of the pectinate muscles.
QBReview: Review this Lesson
The heart has a left and right side separated by a muscular wall (septum). The left and right upper chambers of the heart are the atria. The two lower chambers of the heart are the ventricles. Between the atria and ventricles are valves (AV or atrioventricular valves). Semilunar valves are between the ventricles and the major arteries leaving the heart.