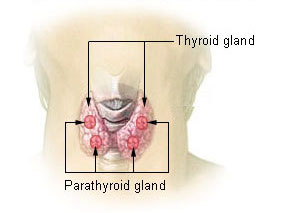
The thyroid gland is located in the neck, below and lateral to the larynx. It secretes thyroid hormones in response to pituitary TSH. Thyroid hormones increase basal metabolic rate by stimulating breakdown of glucose and fatty acids for ATP production, growth, and development. Dietary iodide is required for their synthesis.
Parafollicular cells of the thyroid gland produce calcitonin during growth. Calcitonin stimulates uptake of calcium and phosphates into bone matrix by inhibiting osteoclast activity. Calcitonin does not play a significant role in calcium homeostasis in adults.
Parathyroid glands are small, paired glands on the posterior surface of the thyroid gland. They secrete parathyroid hormone (PTH) which increases blood calcium levels, primarily by increasing osteoclast production. PTH also causes the kidneys to reabsorb more calcium and activate Vitamin D, which promotes intestinal calcium uptake. PTH is the primary regulator of blood calcium in adults.