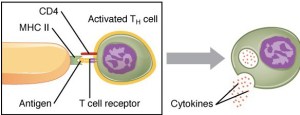
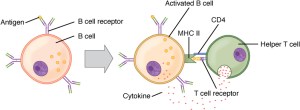
Cell-mediated immunity is carried out by T cells, of which there are two main types: helper T cells and cytotoxic T cells. Antigen-presenting cells (APCs) include dendritic cells, macrophages, and B cells. APCs present antigens to helper T-cells in association with the cell surface molecule, MHC Class II. CD4 receptors on CD4+ T cells recognize the presented antigen and secrete cytokines that can activate B cells to produce antibodies.
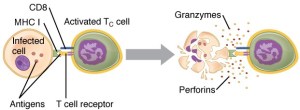
Cytotoxic T cells are derived from CD8+ T cells, which have the CD8 receptor on their surface. These cells carry out cell-mediated immunity and are activated by specific antigens on infected cells presented on MHC Class I cell surface molecules. Cytotoxic T cells kill cells by disrupting metabolism, stimulation of cell death, and formation of large perforin channels.