White blood cells (leukocytes) fight infections and destroy foreign invaders. They may or may not have distinct granules.. Granulocytes are white blood cells with distinct granules in their cytoplasm when stained. Granulocytes include neutrophils, basophils, and eosinophils.
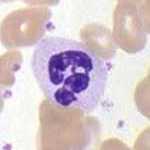
Neutrophils (PMNs, polymorphonuclear leukocytes) have a multi-lobed nucleus and make up about 2/3 of white cells. They arrive first at sites of injury and release factors that attract other white blood cells. Neutrophils are also phagocytes: they engulf pathogens and destroy them by intracellular digestion. Pus is a collection of dead neutrophils and cellular debris.
Eosinophils have a bi-lobed nucleus with pink granules when stained. They recognize antibody-coated invaders and secrete digestive enzymes that digest them extracellularly. Basophils are rare cells with large blue granules that obscure nucleus. They release histamine and heparin at sites of injury.