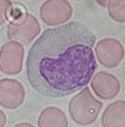
Agranulocytes are leukocytes that do not have prominent granules. Lymphocytes and monocytes are the two types of circulating agranulocytes.
Monocytes have a kidney shaped nucleus and circulate in the blood. When they enter tissues, they become macrophages, giant phagocytes that attack foreign invaders and clean up dead cell debris. Tissue macrophages are resident in tissues and are often given special names: Langerhans cells in skin, osteoclasts in bone, and microglia in the central nervous system.
Lymphocytes are smaller than other white cells and make up about 1/3 of the white blood cell population. Lymphocytes are mostly nucleus. They are classified as T cells, B cells, and NK cells. T cells mature in the thymus and carry out cell-mediated immunity. T cells can be directly cytotoxic or act as helpers for B cells. B cells mature in the bone marrow and carry out humoral immunity (antibody-mediated). NK cells (natural killer) recognize and kill foreign cells in the bloodstream.